ResourceStore configuration options
FileLocationDB
The Location Database provides a mapping between ARC/WARC file names and the absolution location of those ARC/WARC files. Absolute location, in this case, can refer to either HTTP URLs or absolute paths to files on the local file system.
Whenever locations are added for a new filename that was not previously present in the location database, a record (in this case a line) is added to a log file. This log file can then be used to determine which files have been seen by the location database. The ResourceFileLocationDatabase interface includes methods to retrieve the current length of this log file, and to return an iterator with all records between two points in the log. This interface allows an observer to poll the location database to create events when new files are added to the underlying database.
Automatic Indexing Components
Wayback includes 5 Thread/Worker classes to enable automatic indexing
of new content:
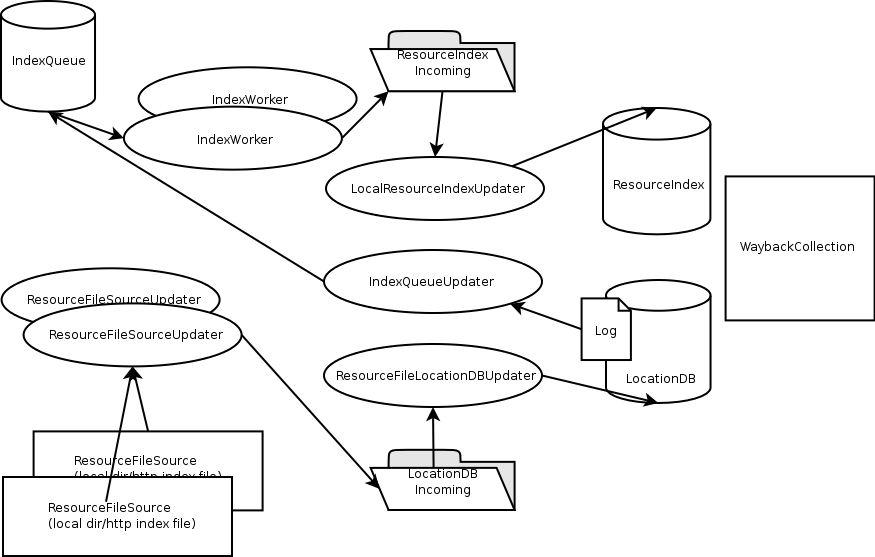
- ResourceFileSourceUpdater is responsible for repeatedly scanning one or more ResourceFileSource instances, creating manifests of the files seen in each, and handing the manifests off to the ResourceFileLocationDBUpdater. In the future, for larger installations, with 100s to 1000s of machines holding ARC/WARC files, multiple instances of this component may run in parallel.
- ResourceFileLocationDBUpdater is responsible for noticing new manifests appearing in an incoming directory, and merging the contents of those manifests with the actual location database, which is currently implemented using a BDBJE database.
- IndexQueueUpdater is responsible for polling the location database log, and adding newly discovered ARC/WARC files to the IndexQueue.
- IndexWorker is responsible for polling the IndexQueue, and when file names are present in the queue, creating an index of all resources in the ARC/WARC file, and handing the results to the LocalResourceIndexUpdater. In the future, for larger installations, multiple instances of this component may run in parallel on multiple hosts, or this entire component may be replaced by a distributed Hadoop indexing implementation.
- LocalResourceIndexUpdater is responsible for noticing new index result files appearing in an incoming directory, and merging those results with an existing LocalResourceIndex. Currently the only provided LocalResourceIndex that can be updated based on an underlying BDBJE database, but future implementation may maintain a set of sorted CDX files, or a combination of CDX files and a BDBJE database.
org.archive.wayback.ResourceStore implementations
Wayback allows for several configurations enabling diverse collection sizes and distribution of ARC/WARC files across many local directories or across many servers. For most configurations, the default LocationDBResourceStore will suffice, but Wayback is distributed with 2 additional classes, FileProxy and SimpleResourceStore, which provide an opportunity to insert a single HTTP caching server between the Wayback service and an ARC/WARC storage cluster.
LocationDBResourceStore
This implementation uses a LocationDB to convert ARC/WARC filenames into absolute paths, or HTTP URLs. The underlying LocationDB can be managed by the automatic indexing threads as described above, or it can be manually managed with the location-client command line tool. Be sure to enable the org.archive.wayback.resourcestore.locationdb.FileProxyServlet if you plan to manage the LocationDB manually.
SimpleResourceStore
This configuration depends on all ARC/WARC files appearing within a single HTTP 1.1 exported root directory, or within a single local directory. ARC/WARC file names are appended to a common prefix, either a local directory on the host running Wayback, or under a single remote directory.
The FileProxyServlet can be used to make all ARC/WARC files accessible within a single HTTP directory, acting as a reverse proxy to the actual host holding the ARC/WARC files. The FileProxyServlet uses a LocationDB to translate requested ARC/WARC filenames into the actual location of each file.
Telling Wayback where to look for your ARC/WARC files
When using the automatic indexing functionality, you need to provide a list of ResourceFileSource objects to the ResourceFileSourceUpdater class. Wayback currently contains 2 ResourceFileSource implementations:
- DirectoryResourceFileSource will recursively scan a local directory for ARC/WARC files (ending with: .arc, .arc.gz, .warc, or .warc.gz). The 'name' property of each DirectoryResourceFileSource must be unique, and consist of valid filename characters.
- JspUrlResourceFileSource is a highly experimental implementation which executes a local .jsp file, passing the 'url' parameter to the .jsp. The local .jsp is expected to produce output of the form (NAME URL) for all ARC/WARC files appearing under the argument url prefix, presumably by parsing the directory index HTML from the server hosting 'url'.


